
Modeling of Electromagnetic Noise from Electronic Devices and Electrical Appliances and Investigation of Mechanisms of Interference
Effects of Harmonics from Spread-Spectrum Clock Systems on Wireless Communications
Today, microprocessors are found in personal computers, office appliances, and many digital home electrical appliances, and the harmonics of the respective clock signals are emitted over a wide frequency range. Recent years have seen the development of spread-spectrum clock (SSC) techniques, which widens the frequency band by sweeping the clock frequency. SSC techniques have been adopted in many electronic devices, since its use reduces the maximum amplitude of measured noise spectrum; however, this does not mean that noise power is reduced. Further, we have yet to clarify the precise consequences of the SCC in terms of the effects of electromagnetic interference caused by radiated noise on nearby wireless systems. Our group is therefore currently investigating the results of the introduction of the SCC method, for noise spectra as well as for a variety of wireless systems.
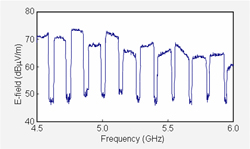
Spectrum of frequency-swept harmonics
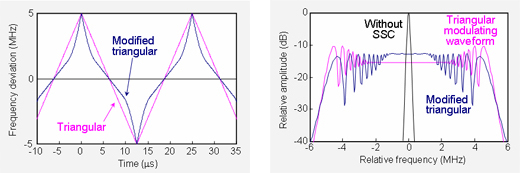
Frequency variation pattern of spread-spectrum clock (left) and harmonic spectrum (right) modulating frequency: 40 kHz, maximum frequency deviation: 5 MHz, resolution bandwidth: 100 kHz.

Bit-error rate (BER) degradation in wireless LANs (IEEE802.11a) caused by spread-spectrum clock harmonics. Interference-to-noise ratio (INR) dependency (left), and maximum frequency deviation (fm) dependency (right).
Modeling of Microwave-Oven Noise and Effects on Wireless Communications
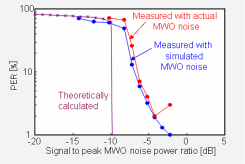
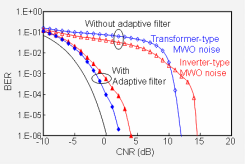
A microwave oven uses frequency band centered around 2.4-GHz for cooking, and a portion of electromagnetic wave generated leaks to the exterior, causing adverse effects on surrounding wireless systems such as wireless LANs and Bluetooth systems. We have performed the world’s first time-domain modeling for describing microwave-oven noise properties; using this model, we have evaluated the effects of the noise on various wireless systems and have investigated methods of reducing interference.
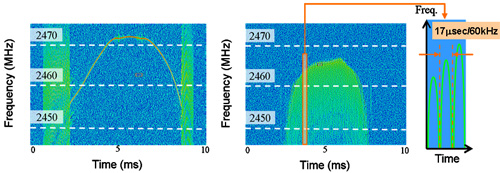
Changes in noise frequency for transformer-type (left) and inverter-type (right) microwave ovens
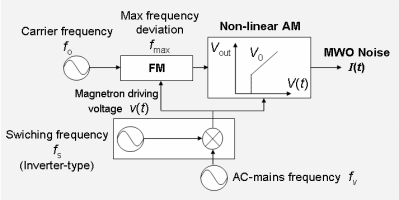
Configuration of the microwave-oven noise model
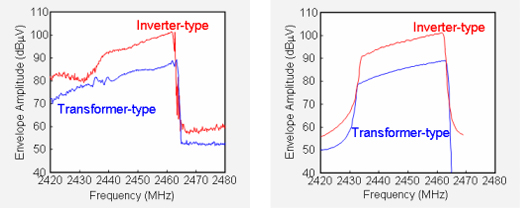
Changes in noise frequency for transformer-type (left) and inverter-type (right) microwave ovens
Effects of power density distribution measurement on DS-UWB transmitter (no partition in front of transmitter)
Effects of power density distribution measurement on DS-UWB transmitter (with partition in front of transmitter)